reduction of area tensile test z|what is reduction of area : factory the reduction of area in the transverse tensile test and the risk of lamellar tearing in joints of differing restraint. This is presented in tabular form in Table 1. z Annex F also contains advice . Temporada 1. Tamara, una filósofa feminista y rockera, se reencuentra con un pasado que creyó haber dejado atrás. IMDb 6,1 2022 10 episodios. X-Ray HDR UHD 18+.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Consulta el número ganador, la serie y los premios de la Lotería del Cauca del último sorteo. También puedes ver los resultados anteriores, las estadísticas y el número de la suerte.
what is reduction of area
Reduction of area is the proportional reduction of the cross-sectional area of a tensile test piece at the plane of fracture measured after fracture. R a = A i - A f A i ⋅ 100. where. R a = Precent reduction of area. A i = Cross ectional area . through thickness properties include through thickness tensile strenght and area of reduction. Some standards limit material through thickness tensile strength shall have min. .the reduction of area in the transverse tensile test and the risk of lamellar tearing in joints of differing restraint. This is presented in tabular form in Table 1. z Annex F also contains advice .
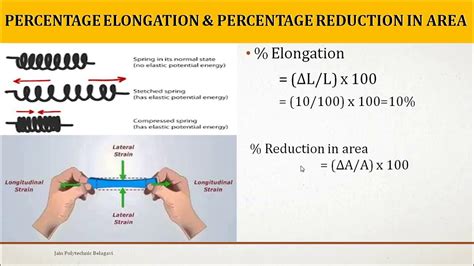
The necking Z is defined as the relative reduction of the cross-section compared to the original cross-section. For example, to meet the Z35 quality level, three test samples must achieve an average cross-sectional reduction of at least 35%. .
8.1.2 Through thickness properties are characterised by specified values for reduction of area in a through thickness tensile test. 8.1.3 Provision is made for two grades Z25 and Z35. For normal .
The test involves applying tensile forces on a test specimen whose axis is perpendicular to the rolled surfaces of steel plate. The primary purpose of the test is to measure resistance to lamellar tearing by determining reduction of area .Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials governs the determination of Ultimate Tensile Strength, Yield Strength plus Elongation and Reduction of Area which are . Determination of percentage reduction of area Z with ZwickRoell AllroundLine testing machine Z250 SN and non contact extensometers according to ISO 6892-1 method A1 closed loop .more.
In addition to fracture strain, the so-called reduction in area \(Z\) also provides information on the deformation behavior of materials. This deformation parameter is determined by the ratio of the reduction in cross .
Zhang et al. [28] analyzed the relationship between area and thickness reduction during a tensile test, observing that the total the ratio ΔA/A0 can be decomposed into a proportional term and a .The necking Z is defined as the relative reduction of the cross-section compared to the original cross-section. For example, to meet the Z35 quality level, three test samples must achieve an average cross-sectional reduction of at least 35%. .
RA% is a term that stands for “reduction of area percentage.” . When fasteners undergo mechanical testing, they are pulled to failure and the diameter of the point at which the fastener breaks is measured and compared to the original diameter. . @Koushik- The concern when yield and tensile are quite close is that the fracture method may . Example Calculation: Let’s say you start with an initial area (IA) of 100 cm² and after a test or process, the final area is 60 cm². The total reduction in area (TR) is the difference between the initial and final area, which is 100 − 60 = 40 100 – 60 = 40 100 − 60 = 40 cm². Using the formula, we can calculate the reduction of area (ROA).Explore the European EN 10002 standard for tensile testing of metallic materials, including terms, definitions, and designations for tests conducted at ambient temperature. Free Trial Login. . Z % Percentage reduction of area: (S o - S u) / S o x 100 : 12. - - Gripped ends :Download scientific diagram | Results of the tensile test: the reduction of the area Z (%), values of the micro-hardness and average micro-hardness í µí±¯í µí±½ , and the speed of the .
Learn how to conduct a uniaxial tension test, what is it, and why it is important in engineering! View and example lab report with procedure and findings. . Ductility is also measured by Area Reduction (AR): another measure of ductility is the percent reduction in the area defined as AR% =[(A o – A f)/ A o]x100.The %EL is specific to the tensile testing standard, particularly the ratio of the diameter of a round bar tensile specimen to its parallel length (and to the specified test conditions, rate etc.).
reduction of z
Through thickness tensile test or ‘Z’ direction tensile test is performed to evaluate mechanical properties mostly in steel. The test involves applying tensile forces on a test specimen whose axis is perpendicular to the rolled surfaces of steel plate. The primary purpose of the test is to measure resistance to lamellar tearing by determining reduction of area and ultimate tensile .The maximum stress that the material can withstand before breaking is the ultimate tensile strength. Reduction of area and percent elongation can be calculated from the broken sample. . due to strain hardening is balanced by the decrease in load-carrying ability due to a decrease in the cross-sectional area. In a tensile test, this maximum in .Reduction of Area. Measure of the ductility of metals obtained in a tensile test. It is the difference between original cross sectional area of a specimen and the area of its smallest cross section after testing. It is usually ex-pressed as % decrease in original cross section. The smallest cross section can be measured at or after fracture. This contribution deals with the use of maximum thinning and reduction of sample cross section area at fracture after tensile testing and applications for industrial flat sheet steels. Although included in all usual tensile testing standards, this mechanical property ("Z-value") has long been neglected for flat sheet materials.
The quantities commonly used to define ductility in a tension test are relative elongation (in percent, sometimes denoted as ) and reduction of area (sometimes denoted as ) at fracture. [16] Fracture strain is the engineering strain at which a test specimen fractures during a .
In the equation for stress, P is the load and A 0 is the original cross-sectional area of the test specimen. In the equation for strain, L is the current length of the specimen and L 0 is the original length. Stress-Strain Curve. The values of stress and strain determined from the tensile test can be plotted as a stress-strain curve, as shown below: Exploring Elongation TestingElongation testing, a cornerstone of material science, reveals a material's ductility and strength when under tensile stress. By stretching a sample until it breaks, this test measures how much a material can deform before failing. In industries prioritizing safety and durability like automotive and construction, this insight is crucial. .The tensile test is a test method within mechanical materials testing, used for the determination of material characteristics.Depending on the material, the test is used in accordance with the respective industry standard for determination . Tensile or tension testing is a fundamental and most commonly used test for the characterization of the mechanical behavior of materials. The test consists of pulling a sample of material and measuring the load and the corresponding elongation. . The second measurement of ductility is defined as the percentage reduction in area, %RA. It is .
The tensile test procedure involves attaching the sample to the testing machine and applying force until the material fractures. The results are typically recorded in a stress-strain diagram. . Similarly, reduction of area, Z is the largest remaining cross-section change referred to the initial section after fracture of the test specimen.Pf ≡ final load carried by the specimen during the test, N (lb) A0 ≡ original cross-sectional area of specimen, mm 2 (in.2) • Calculate the reduction of cross-sectional area. 0 0 %Reduction 100f AA A − =× (1.1.5) where: Af ≡ cross-section after failure, mm 2 (in.2) To calculate the cross-section after failure, fit the ends of the .
This contribution deals with the use of maximum thinning and reduction of sample cross section area at fracture after tensile testing and applications for industrial flat sheet steels. Although included in all usual tensile testing standards, this mechanical property ("Z-value") has long been neglected for flat sheet materials.elongation, tensile strength, elongation, and reduction of area. 1.2 The gauge lengths for most round specimens are re-quired to be 4D for E8 and 5D for E8M. The gauge length is the most significant difference between E8 and E8M test . original cross-sectional area of a tension test specimen and the area of its smallest cross section.Reduction of Area. Measure of the ductility of metals obtained in a tensile test. It is the difference between original cross sectional area of a specimen and the area of its smallest cross section after testing. It is usually ex-pressed as % decrease in original cross section. The smallest cross section can be measured at or after fracture.
ABS Grades A, B, D, and E Z35 are "Z" quality, ordinary-strength structural steels with a minimum specified yield strength of 34 ksi and specified minimum Charpy V-notch impact toughness properties. The Z35 quality steel has a minimum specified average value for reduction of area in through-thickness tensile testing of 35%. Applications
Tensile Test adalah pengujian tarik yang bertujuan untuk mengetahui Kekuatan luluh, kekuatan maksimum material. . Reduksi penampang/reduction of area (RA ) RA=[(A0-A1)/A0] 100% . dimensi Width (W) sebesar 0.5 inch (12.7 mm) dan lebar area cekam sekitar 3/4 in. (19.05 mm). Dibagian tengah dari batang uji (bagian yang paralel) adalah bagian .
1.1 This specification 2 covers the procedures and acceptance standards for the determination of reduction of area using a tension test specimen whose axis is perpendicular to the rolled surfaces of steel plates 1 in. [25 mm] and greater in thickness. The principal purpose of the testing is to provide a measure of the resistance of a steel .Through-Thickness Tension Testing, “Z” Quality. When “Z” quality steel is specified, through-thickness tension testing is performed in accordance with ABS Rules and ASTM A770. Two “Z” quality steels are available, Z25 and Z35. The through-thickness tension testing reduction of area requirements for each are tabulated in the table. I do experienced tensile test of API 2W materials which is thermomechanically rolled and normally used for offshore structure, very good toughness which can have more than 200J @ -40 degree C. i was wondering when we did the transverse weld tensile test and it shown fracture at parent metal with relatively large elongation and reduction of area .
8 de fev. de 2022 · Anomalous Activities is a 1v12 Asymmetrical shooter with horror elements, a focus on satisfying gunplay, teamwork, impactful gameplay and a skill .
reduction of area tensile test z|what is reduction of area